Project Description
In the previous article, our Technical Team focused on explaining how cyber security has become a critical aspect of the modern technological landscape, particularly in sectors like automotive, where In-System Programming (ISP) is widely used.
This guide helps you implement cyber security features on FlashRunner Workbench.
How to implement Cyber Security in Workbench?
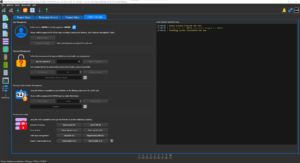
Within our user interface, the Workbench, we have a dedicated section for Cyber Security.
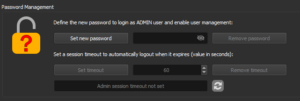
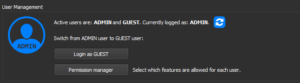
By entering a password and clicking on “Set new password” the user management mode is activated. It’s important to remember the password, as it will be required each time to log in as Admin.
The two types of accounts available are Admin and Guest.
The Admin account, through the permission manager, can select which commands can and cannot be executed by the various users.
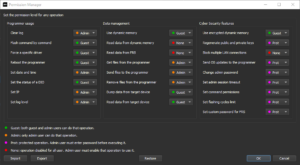
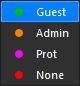
By choosing between the 4 options:
– Guest: the command can be executed by both Guest and Admin.
– Admin: the command can only be executed by Admin.
– Prot: the command requires password entry to be executed.
– None: no user can execute the command, as it is blocked.
By clicking on “Remove password” and entering the Admin password, the user management mode is deactivated.
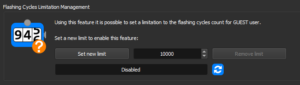
Flashing Cycles Limitation Management can be configured by logging in as Admin and allows setting a maximum number of cycles for Guest mode.
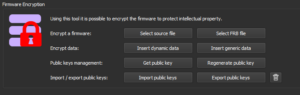
Firmware Encryption is a feature always available directly from the Workbench. It allows encrypting the firmware before flashing it onto the device to protect the intellectual property of the firmware.